On 4 October local time, the European Union held a vote on whether to impose a five-year countervailing duty on Chinese electric cars, and although the motion was opposed by Germany and other countries, it was ultimately passed by a 10:4 vote. The new regulations will come into force in November this year, and up to 45 per cent of tariffs will be imposed on electric cars imported from China into the EU.
The 10 countries that voted in favour include Bulgaria, Denmark, Estonia, France, Ireland, Italy, Lithuania, Latvia, the Netherlands and Poland, according to a report by Euronews. (45.99 per cent of the EU's total population); the 12 countries that abstained included: Belgium, Czech Republic, Greece, Spain, Croatia, Cyprus, Luxembourg, Austria, Portugal, Romania, Sweden and Finland. (31.36 per cent of the total population of the EU); five countries were against: Germany, Hungary, Malta, Slovenia and Slovakia. (22.65 per cent of the total EU population).
The European Commission's proposal to impose final tariffs on Chinese-made electric cars has the support of enough member states, it said in a statement.
The EU believes that the Chinese government's massive subsidisation of its own electric car industry, by which it creates a cost advantage and then exports them to Europe at low prices, creates unequal competition for the European auto industry, and has therefore decided to counteract it by imposing tariffs.
Mario Draghi, president of the European Central Bank, said China beyond the ‘national financial subsidies’, so that the European Union has become more dependent on China, the future will be difficult to resist the impact of China's electric vehicles. Data show that in 2023, the EU and China's trade volume reached 815 billion U.S. dollars, is China's largest trading partner.
In recent years as China's auto industry has rapidly shifted to electrification and intelligence, it has now established a strong industrial chain advantage and cost advantage, compared with Europe, as the town of many traditional fuel car companies, which has been slow to transition to electric vehicles and has gradually declined in the competition with Chinese electric car brands.
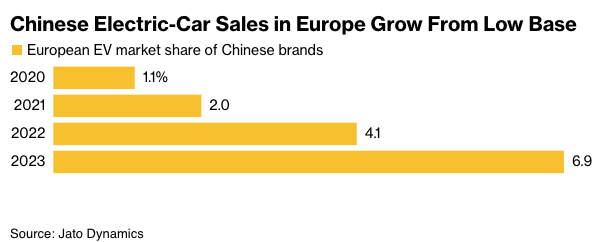
According to Jato Dynamics data, China's EV sales share in the European market has grown rapidly from 1% in 2020 to 6.9% in 2023.
Against this backdrop, on 4 October 2023, the European Commission initiated a countervailing duty investigation into imports of electric vehicles from China, and on 4 July 2024, it began to impose provisional countervailing duties on Chinese electric vehicles. on 20 August, the EU released a draft final ruling on the countervailing duty investigation into Chinese electric vehicles, indicating that it proposed to impose countervailing duties ranging from 17% to 36.3% on Chinese electric vehicles.
The latest finalised rates show that the EU will add 7.8 per cent on Tesla, 17 per cent on BYD, 18.8 per cent on Geely, 35.3 per cent on SAIC, and 20.7 per cent on other electric vehicle producers involved in the investigation but not sampled separately. Europe currently has a 10 per cent tariff on car imports, meaning that Chinese EV makers will face an extraordinarily high tariff of up to 45 per cent when entering the European market.
The European Commission added that it will meanwhile continue negotiations with China ‘to explore an alternative solution, which must be fully WTO-compliant, adequately address the damaging subsidies identified by the Commission's investigation, and be monitorable and enforceable.’
Declaration: This article comes from the ChinaAET.If copyright issues are involved, please contact us to delete.